The back, including the spinal cord, is one of the most structurally vital parts of a person’s physique as it supports the torso and allows a person to stand upright. If something goes wrong with the back, it can leave a painful or debilitating condition that can keep anyone from doing the things they love.
While most back problems manifest as people get older, a condition that starts early on—in childhood or early adolescence—affects 2% to 3% of the population in the U.S. alone: scoliosis
To know more about this condition and find out how to address it, check out the infographic.
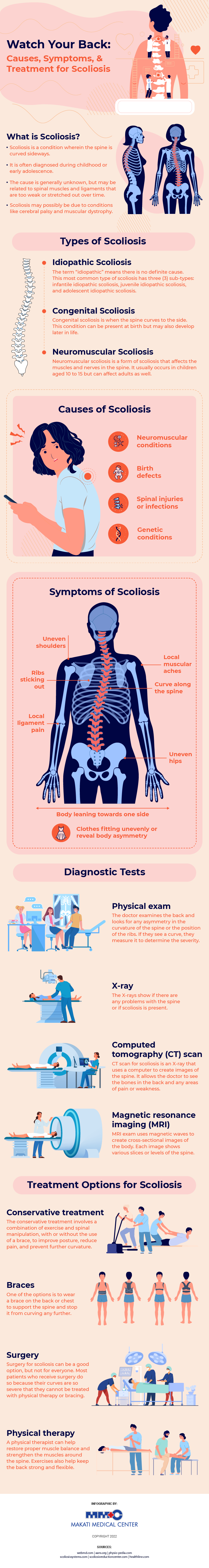
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine curves to the side. It is usually diagnosed among adolescents and young adults but can occur at any age. Scoliosis can be mild or severe and affect one or both sides of the spine.
The most common symptom is back pain. In many cases, this is caused by unequal weight distribution on each side of the spine. A person with Scoliosis may also experience shoulder and hip pain and problems with balance and coordination.
Some people with milder forms of scoliosis may not notice any symptoms until they reach adulthood when their bodies are fully developed.
Types of Scoliosis
1. Idiopathic Scoliosis
Idiopathic Scoliosis is a curved spine that is present from birth. It can happen to anyone but most often affects children and adolescents.
The main symptom of Idiopathic Scoliosis is a curve in the spine that results in an unevenly shaped back. In some cases, the affected individual may not have any symptoms, but others may experience pain or discomfort in their back or neck region.
The cause of Idiopathic Scoliosis is unknown; however, it is typically thought to be genetic in nature, passed down from one generation to the next. It can also be due to other factors such as having weak muscle tone, having poor posture while standing or sitting upright, or being overweight or obese, which causes excess burden on the spine.
2. Congenital Scoliosis
Congenital Scoliosis is spine curvature caused by genetic factors but can also be due to malnutrition or trauma to the fetus during pregnancy. During fetal development, the spine’s vertebrae may fail to develop properly.
Congenital Scoliosis may correct itself by adolescent age, but in case it does not, treatment may be required to straighten the curvature.
3. Neuromuscular Scoliosis
Neuromuscular Scoliosis affects the spine and other parts of the body. This happens when there is damage to the nervous system, causing problems to the muscles and nerves.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis can bring pain in the back and neck area, as well as problems with balance and muscle strength. The symptoms will vary from person to person, depending on the damage to the nervous system.
What Causes Scoliosis?
1. Neuromuscular conditions
Neuromuscular conditions are often characterized by muscle weakness or paralysis. This is why they are sometimes referred to as “neurological” disorders. Some examples of neuromuscular conditions include muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy.
These disorders can lead to Scoliosis because they cause muscles in the back to weaken or stop working altogether.
2. Birth defects
The causes of Scoliosis can be traced back to congenital disabilities, which can manifest in many ways.
This condition happens early during pregnancy when the fetus’ vertebrae in the spine do not form properly, which leads to a hemivertebrae or a sharp angle in the spine. There are cases where two (2) or more vertebrae do not separate fully, leading to spinal deformity.
3. Spinal injuries or infections
Spinal injuries or infections can cause disc degeneration, which leads to spinal curves that may be severe enough to require surgical intervention. The most common types of spinal injuries are fractures, sprains, and contusions. These can occur during car accidents, falls from heights or stairs, sports injuries, including concussions, and more.
4. Genetic conditions
One of the most common factors of back problems is genetic conditions. When a child inherits specific genes from their parents, they are at risk of developing Scoliosis. These conditions can cause abnormal bone growth and development, leading to Scoliosis and other physical problems like weak muscle or short stature.
Signs and Symptoms of Scoliosis
1. Uneven shoulders
Having uneven shoulders could mean one shoulder is higher than the other. It occurs because of a curve in the spine that causes the vertebrae to shift, resulting in a sloped appearance. It can also be caused by poor posture or other physical issues.
2. A curve along the spine
One may have Scoliosis if they have a curved spine because their vertebrae are out of line. This can be physically obvious and is usually accompanied by imbalanced or skewed shoulders.
3. Uneven hips
A person with Scoliosis has a spine that curves in a way that makes their upper body appear to be leaning to one side while their lower body seems to be straight. This causes the hip bones to shift into different positions, resulting in uneven hips.
It can cause pain and discomfort in the areas where muscles are positioned at an awkward angle, which may lead to reduced mobility.
4. Ribs sticking out
A rib hump is another indicator of Scoliosis but may also be due to other conditions, like arthritis and osteoporosis. The ribs are connected to the spine, forming a chest wall that protects the internal organs. An irregularity in the spine causes the ribs to stick out.
The condition is often accompanied by other symptoms, including back pain and breathing difficulties.
5. Local muscular aches
Local muscular pains occur because the spine changes shape and puts stress on the muscles around it. The muscles become strained or stretched out, which results in pain or tightness in those areas. The pain can be sharp or dull and range from mild to excruciating, depending on the severity of Scoliosis.
6. Local ligament pain
The ligaments are bands of connective tissues connecting the vertebrae and holding them in place. When they are overstretched or strained due to abnormal spine curvature, they can become painful to touch or pressure.
Local ligament pain can be treated by stretching exercises that focus on strengthening these muscles and ligaments while gently relaxing them.
7. Leaning towards one side
The body tends to compensate for the imbalance caused by Scoliosis by shifting weight to one side. A person may also notice this same symptom if they sit down for long periods at work, school, or home. This restricts movement, causing pain and discomfort in varying degrees, depending on the condition’s severity.
8. Clothes fitting unevenly
A curved spine creates a hump at the base where the ribcage meets the pelvis when a person bends forward. This hump can cause clothing like shirts and pants to hang wrong, which means they do not fit right and appear uncomfortable to wear.
Diagnostic Tests
1. Physical exam
A physical exam is conducted to determine the exact size and location of the spine’s curvature. It is checked and assessed for deformity, muscle weakness, and abnormal disc spaces.
The primary screening exam is called the Adam’s test or the forward bend test, where a patient is asked to remove their shirt so that the spine is fully visible. They are then asked to bend forward with knees straight, feet together, and arms hanging freely. This position allows the doctor to check for the following:
- The visible curve of the spine
- Asymmetries in the shoulders and hips
- Humps in one side of the rib cage
2. X-ray
X-ray for a Scoliosis patient is performed the same way as with any other patient. The only difference is that the patient’s spine will be exposed in full view of the Radiologist.
3. Computed tomography (CT) scan
A CT scan is a non-invasive scanning procedure that captures detailed images of specific parts of the body. The CT scan takes pictures of body parts from different angles and combines them into one image. This allows doctors to see how bones fit together in specific areas and detect any abnormalities affecting their alignment.
4. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
An MRI exam takes multiple images of a Scoliosis patient’s spine using a machine with powerful magnets and radio waves to produce a detailed picture for a more accurate diagnosis. The procedure takes between 15 and 90 minutes, depending on the size of the body part and how many images need to be taken.
Treatment Options for Scoliosis
1. Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment for Scoliosis aims to prevent further curvature of the spine and improve posture. The goal is to keep the patient from needing surgery. Doctors may recommend this treatment if the curve is not severe and the symptoms are mild.
Conservative treatments include physical therapy that may involve braces or corsets to strengthen muscles, improve posture, and stop spinal curves from worsening.
2. Braces
Braces are one of the most common ways to treat scoliosis. They work by making the spine straighter, making it easier for the patient to move their body comfortably. They can be made of metal or plastic and come in different shapes and sizes.
Some braces are worn over clothes while others are worn under. A doctor or physical therapist can customize them for a better fit, which is crucial in providing support throughout the day without pain and discomfort.
3. Surgery
Surgery may be performed on the neck or lower back to correct Scoliosis. In some cases, only a specific section of the spine is affected; in others, multiple parts need correction. Spinal fusion is performed on Scoliosis patients. This allows doctors to realign and fuse curved vertebrae, healing into one solid bone.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy helps treat Scoliosis patients by strengthening their muscles and improving posture to straighten the spine. It also enhances body coordination while also reducing pain and improving balance.
Physical Therapists can help patients learn ways to make everyday activities easier for their back through proper posture and avoiding movements that cause pain or worsen symptoms.
We Have Your Back
Scoliosis is a common spine condition that can result in long-term health problems if left untreated. The best way to prevent these complications is to seek treatment immediately. Early detection can help a patient avoid orthopedic surgery later on.
Makati Medical Center offers its patients world-class facilities and healthcare services from the best medical professionals. For all medical needs, visit our website today.