Finding out that you or a loved one has been diagnosed with cancer is probably one of the worst news you will ever receive. Symptoms and treatment vary per type, and to date, there is no known cure for the deadly disease.
Cancer is a blanket term for diseases causing abnormal cell growth. Healthy cells malfunction and mutate to a condition and usually affects a specific part of the body. However, if left untreated or unchecked, it has the potential to spread or metastasize. At this stage, the cancer is probably already fatal.
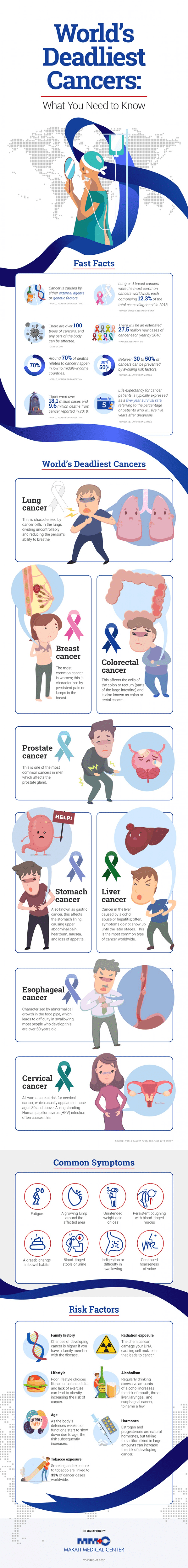
Educating yourself about cancer is one way to catch it in its early stages or prevent it from developing into something worse. To understand more about the disease and its impact worldwide, here is a detailed fact sheet of the most common types of cancer, their symptoms, and risk factors.
The World’s Deadliest Cancers
1. Lung cancer
Lung cancer is the number one cause of death related to cancer worldwide. Smoking cigarettes and even exposure to secondhand smoke are the most common risk factors for developing the disease. The battle against lung cancer is one of the most difficult, as it is usually detected once it has spread.
The five-year survival rate for lung cancer cases detected at an early stage is 56%. This means the disease is still localized in the lungs. However, only 16% of cases are detected this early. Once it has spread to other organs, the survival rate lowers to 5%.
Treatment options for lung cancer include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, or a combination of these.
2. Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer—also known as colon cancer, rectal cancer, or bowel cancer—usually begins in the large intestine and affects older adults. Benign lumps, called polyps, form inside the colon and show very few symptoms. Over time, these can become malignant.
The average five-year survival rate for colorectal cancer is 65%. If detected at a localized stage, the figure increases to 90%. Around 39% are diagnosed at a stage this early. The most common treatment options for it are radiation therapy, surgery, and chemotherapy.
3. Breast cancer
Breast cancer is the most invasive cancer found in women. While its cause is unclear, a common risk factor is extended exposure to estrogen. This could be through pregnancy, hormone therapy, early puberty, or late menopause.
The average five-year survival rate for women with advanced stages of breast cancer is 90%, and the ten-year survival rate is 83%. The chances increase to 99% when it is still localized in the breast; 62% of women are diagnosed at this stage.
Surgery to remove the whole breast, called a mastectomy, is the most common way to treat the disease in its advanced stages. A lumpectomy, which is a less aggressive treatment, aims to remove the tumor and its surrounding tissues only. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are both common treatment options to kill breast cancer cells.
4. Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancers diagnosed in men but is less severe than the other kinds in this list. It usually grows slowly, to the point that some may only need minimal or no treatment. However, this does not rule out the possibility of developing the aggressive form of the disease.
Prostate cancer is highly treatable. Finding it in its initial stages gives patients a five-year survival rate of 100%, a ten-year survival rate of 98%, and 96% for 15 years. For advanced stages, the most common treatments are surgically removing the prostate and seminal vesicles, and radiation therapy such as external-beam radiation therapy and proton beam therapy.
5. Stomach cancer
Also known as gastric cancer, this affects the stomach lining. It causes upper abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, and loss of appetite to the affected patient. These are also the most common symptoms in its early stages.
If found at an early stage where the cancer is only in the stomach, there is a five-year survival rate of 65%. If it has spread to surrounding organs, this figure drops to 30%. Treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, targeted drug therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
6. Liver cancer
Several types of cancer can develop in the liver. The most common is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the hepatocyte, the primary cell of the organ. Symptoms of liver cancer can include loss of appetite, unintentional weight changes, general fatigue, jaundice, nausea, and vomiting, to name a few.
Hepatitis, liver diseases, and excessive alcohol consumption are the main risk factors of the disease. The average five-year survival rate of cases found early is 31%. If it has metastasized, this drops to 11%.
Standard treatment options include liver transplant surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Localized treatments include heating or freezing cancer cells and injecting pure alcohol or chemotherapy drugs into the liver.
7. Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer grows in the food pipe or gullet and mainly affects people in their 60s or 70s. It is also more common in men. It presents itself in symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing, heartburn, indigestion, and vomiting. Smoking, drinking too much alcohol, and having gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) are the most common causes.
Localized cases have a five-year survival rate of 45%, while those in the advanced stages only have 24%. In its final stage, this drops to 5%.
Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the affected section of the esophagus, called an esophagectomy. In advanced stages, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can slow the spread and ease the patient’s symptoms.
8. Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer occurs in the cells of a woman’s cervix—the part that connects the uterus to the vagina. The most common cause of developing the disease is being infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). However, all women are still considered at risk. It is usually more common for those 30 years old and above.
The five-year survival rate of the disease is 92% when detected at an early stage. Around 45% of women get this initial diagnosis. If it has spread or metastasized, the figure decreases to 56%.
Localized treatment for cervical cancer includes destroying the cells through cold knife conization and loop electrosurgical excision procedure or LEEP. In advanced stages, surgery and radiation therapy are most common.
A vaccine is also available to prevent HPV infection. It can be given to both boys and girls as early as 9 years old for prevention of cancer-causing infections and precancers.
Be One Step Ahead of Cancer
Cancer may be a deadly disease, but it is avoidable. Lower your chances of developing it by making healthier lifestyle choices, taking good care of yourself, and getting vaccinated (hepatitis and HPV). It also helps to know more about cancer care so you can look after your loved ones suffering from this disease better.
If you have a high risk of cancer or believe that you are exhibiting signs of the disease, do not hesitate to get yourself checked. Makati Medical Center has a reputable cancer center with doctors who can help with prevention, early detection or cancer care, including pain management, for advanced stages.