Many people growing up have had their parents scold them for running around and playing immediately after a meal. This stems from the belief that any strenuous activity, such as running, can lead to a ruptured appendix.
Even if this is just a myth, there are real reasons why an appendix may become sore or swollen that could eventually rupture if not treated immediately. To get to the bottom of this, keep reading to find out what an appendix is, what it does, and the possible causes of appendicitis.
What Does the Appendix Do?
The appendix is a small organ affixed to the large intestine located on the lower right side of the belly.
If the appendix is blocked, inflamed, or ruptured, it is known as appendicitis. Nobody knows its exact purpose, but scientists suggest that it is a place where good bacteria are stored until needed. If left untreated, an infected appendix can cause severe problems.
People who are unfortunate enough to have a ruptured appendix will have to opt for an appendectomy, which is a surgical procedure to remove the appendix.
Possible Causes of a Ruptured Appendix or Appendicitis
Many people ask, “What causes appendicitis?” One of the common causes of appendicitis is a blockage in the lining of the appendix. Other causes include viruses, bacteria, or parasite infection.
Another cause can be a blocked tube that connects the large intestine and appendix. Sometimes, stool can cause this blockage, but tumors can also be a culprit.
If left untreated, the appendix becomes swollen, inflamed, and filled with pus. As the swelling worsens, the blood supply stops, and the appendix potentially bursts or ruptures. When this happens mucus, stool, and the infection can spread to the belly, leading to a more serious condition called peritonitis, or the redness or swelling of the tissues around the abdomen.
Data suggests that 1 in 1,000 people in the U.S. will have appendicitis. Many of the cases come from people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Additionally, a family with a history of appendicitis can increase the risk, especially for men. In the Philippines, deaths from this condition reached 332 in 2018.
The following section further discusses some of the causes and how it affects the appendix:
1. Bacterial infection
Bacterial infection can block the lining of the appendix. It multiplies quickly, leading to inflammation. An inflamed appendix will be swollen and full of pus. It is critical to see a physician immediately for treatment to prevent rupture and leaks.
2. Parasitic infection
Parasitic infections to the appendix are rare, but some parasites that cause appendicitis are Enterobius vermicularis, Schistosoma spp, and Taenia spp. Parasites are living organisms that live off their host’s body, so it is paramount to consult a doctor immediately.
3. Hard stool
As mentioned earlier, a tube connects the appendix and the large intestine. This can be blocked, and one of the causes can be a hard stool.
When this happens, it can cause abdominal discomfort and pain. Get medical attention right away if there are persevering aches and pains in the abdomen before it gets worse.
4. Swollen intestinal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes, or the small organs that help our body recognize and fight germs, can become swollen in the membrane that connects the bowel to the abdominal wall. The condition is called mesenteric lymphadenitis. A common cause is a viral intestinal infection, and it mainly affects children and teenagers.
The pain can mimic appendicitis, which is commonly linked to the condition. Have a doctor evaluate the symptoms and perform tests to ensure a proper diagnosis.
Signs and Symptoms of an Inflamed Appendix
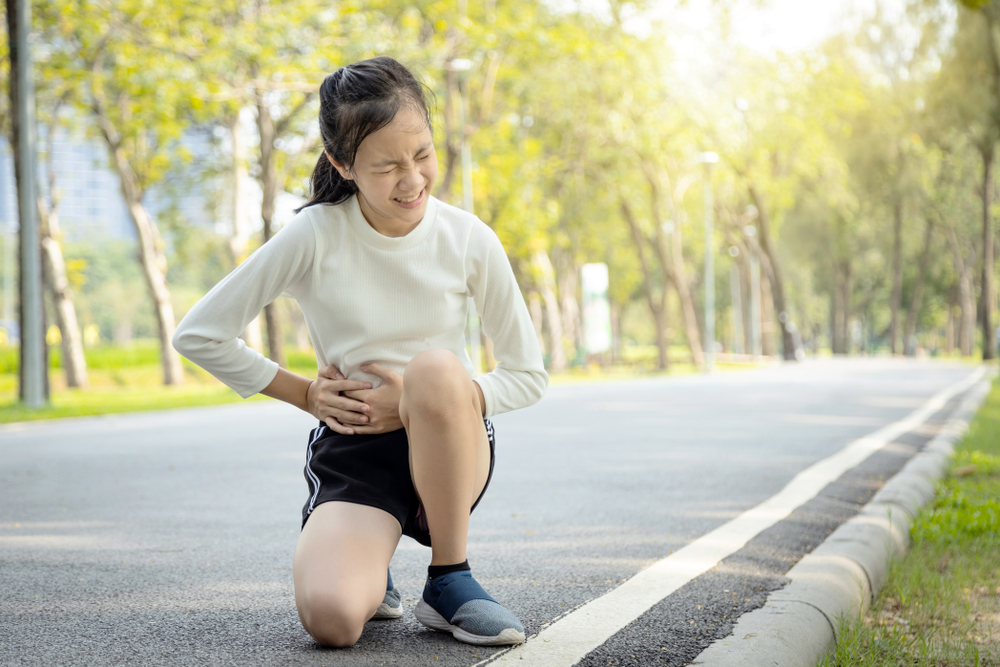
Appendicitis is a serious problem that needs medical attention immediately. If any of the symptoms persist, it would be best to rush to the nearest hospital to receive appropriate treatment:
- Abdominal bloating
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Issues in passing gas
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe cramps
- Sudden pain in the lower right side of the abdomen
- Sudden pain on the right side of the lower abdomen
Diagnostic Tests
Doctors will use a few methods to properly diagnose appendicitis. Below is a short list of procedures and tests that doctors may use:
1. Physical examination
A physical exam will involve a pain test by applying gentle pressure around the bowel area. The pain often feels worse when the pressure is suddenly released. The doctor may use other procedures such as spotting abdominal rigidity (stiffness) and conducting a digital rectal exam to make an accurate diagnosis.
2. Blood test
A blood test may be necessary since the results can check any signs of infection. Other determining factors such as the white blood cell count can help diagnose the condition.
3. Urine test
Urine tests can help rule out a urinary tract infection (UTI) or kidney stones, which can cancel out possible causes of abdominal pain, leading to a more accurate diagnosis.
4. Imaging tests
The doctor may include imaging tests to better understand the cause. Diagnostic imaging tests such as ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done around the abdominal area to confirm if it is indeed appendicitis or some other condition.
Treatment and Recovery
There are two routes that a Gastroenterologist may opt for when treating appendicitis: surgery or antibiotics.
Depending on how severe it is, the doctor may require an appendectomy. Doctors will apply general anesthesia and use a laparoscope (a thin lighted tube that can be inserted into the mouth during the procedure) to help surgically remove the appendix, which involves minor cuts around the belly.
However, if an abscess is present, it may require two procedures, with the first one to clear the pus and the second to remove the appendix, which would need an open appendectomy.
Additionally, research suggests that taking antibiotics can help treat acute or severe appendicitis, which may help people avoid going into surgery.
When Unsure, Visit the Nearest Hospital
Appendicitis is a serious illness that needs immediate treatment. If any symptoms persist, do not wait to see a doctor. Delaying treatment will only make the situation worse and can cause more complications.
Visit the Makati Medical Center for gastrointestinal treatment and other health concerns. The hospital has been providing professional medical care since 1969, and patients are guaranteed to receive the best healthcare services possible with its world-class facilities and highly skilled healthcare professionals.