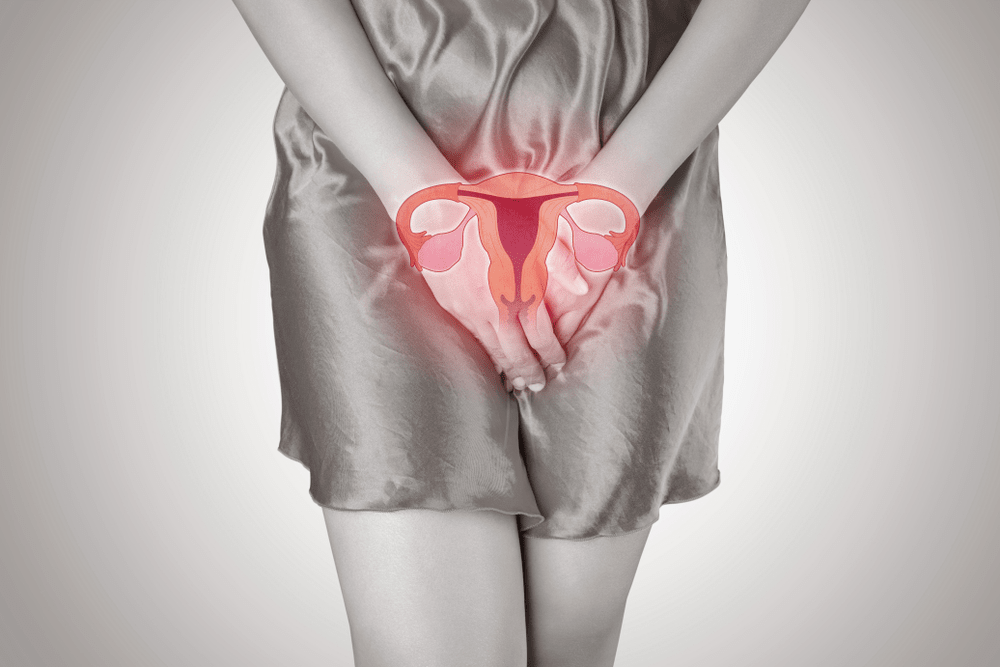
A vast percentage of women may be no stranger to irregular periods, abnormal weight gain, and perhaps the growth of unwanted hair in unusual parts of the body or even hair loss.
Dealing with these conditions can be tough, so it would be best to seek professional help as these are also signs that point to one condition: polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS.
What Is PCOS?
PCOS is a female hormonal disorder affecting the function of a woman’s ovaries. It is a common condition that can affect up to 70% of women, usually between the ages of 15 and 44. These are the so-called reproductive or child-bearing years when the ovaries are producing hormones that prompt women’s monthly menstruation.
The Effects of PCOS on Women
The problem with PCOS is the imbalance in hormones because the body is producing excess levels of certain hormones, causing irregularities in a woman’s menstrual cycle.
PCOS may also lead to the ovaries developing problems, such as eggs not becoming mature enough to trigger ovulation. As such, PCOS can affect the ability of a woman to bear children.
Common Symptoms of PCOS
A PCOS diagnosis needs at least two of the following symptoms:
Irregular periods
Heavy bleeding
Polycystic ovaries
In PCOS, the term “polycystic” means “many cysts,” although having PCOS does not necessarily mean you have cysts in your ovaries.
What polycystic ovaries indicate is that the ovaries have become enlarged and contain many small follicles that may be up to 8mm or 0.3inches in size. Because of these follicles, the ovaries are unable to ovulate or release eggs. Without eggs to be fertilized by a man’s sperm, it will be difficult for women to get pregnant.
Abnormal hair growth or hair loss
Obesity
Boils and lumps
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
There is no single test to diagnose PCOS, so a patient needs to undergo a series of examinations and symptoms check to help an obstetrician-gynecologist (OB-GYN) narrow down the diagnosis. These tests include the following:
1. Physical exam
2. Pelvic exam
3. Pelvic ultrasound
4. Blood test
5. Hysteroscopy and Biopsy
Factors That Play a Role in PCOS
Since the cause of PCOS is not entirely known, it may help to look at the factors that can lead to PCOS instead.
Insulin
Androgen
Progesterone
Treatment
There is no known cure for PCOS, and the best way to deal with it is knowing how to regulate the menstrual cycle, as well as managing other symptoms. These things can help:
- Weight loss. Even if the patient only loses about 5% to 10% of her weight, this is enough to bring about improvements in the way her ovaries work. Include regular exercise and eating a healthy, balanced diet with lots of lean meat, fruits, vegetables, and whole foods to help lose those pounds.
- Birth control. If the patient is not planning to get pregnant just yet, taking medications for birth control can help in regulating hormone levels and, consequently, the monthly period.
- Fertility medications. If a patient does wish to get pregnant, it will be best to discuss this with her doctor first so that she will be given medications that stimulate ovulation.
- Diabetes drugs. These drugs work to regulate insulin levels and help reach an ideal weight, which can improve ovulation.
Being PCOS-Free is Good for the Future
Disorders like PCOS need immediate attention, particularly because it has the potential to affect a woman’s future if she wishes to have a family. At the first sign of any PCOS symptom, take the necessary precaution by going for a medical checkup, so a doctor can help figure out if it’s PCOS and not any other condition with similar symptoms.
For a more accurate assessment, seek professional help from the specialists at Makati Medical Center’s Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology.