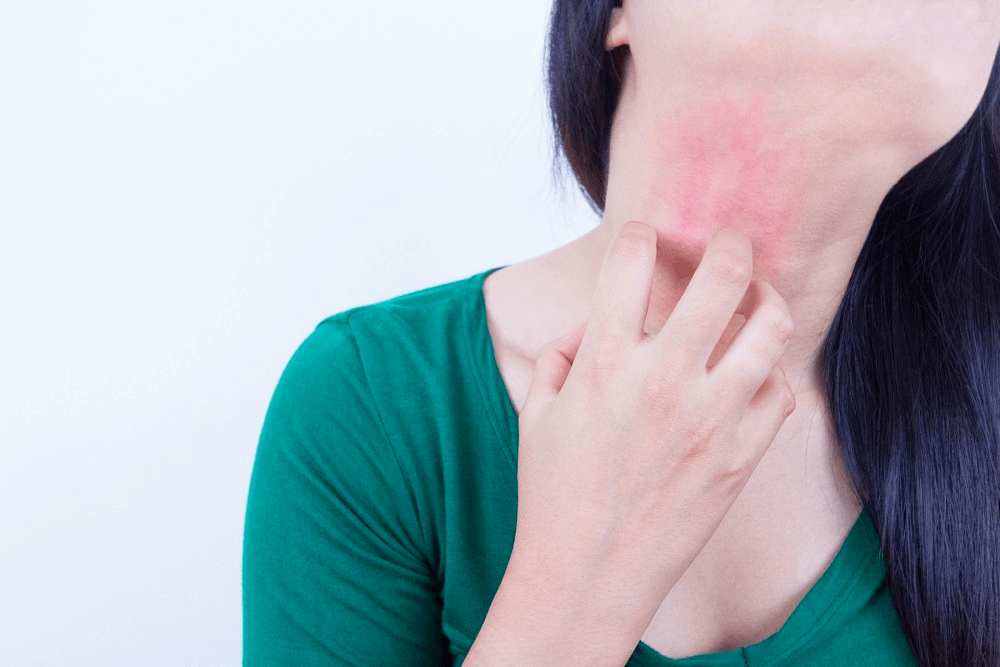
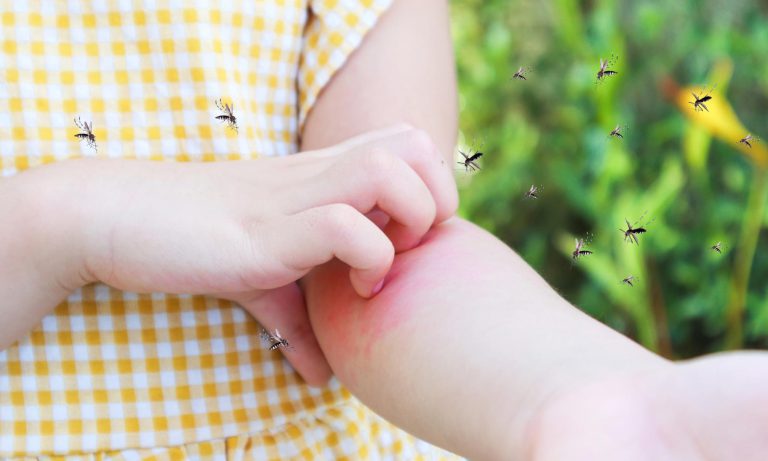
Dust, pollen, insect stings, mold, food, and other allergens can trigger a sudden allergy attack or allergic reaction. Its manifestations can come in various forms, such as sneezing, stuffy or runny rose, skin irritation, and sore throat, among others, which can be extremely unbearable in some cases.
Everyone’s body is different, and the immune system’s response to an allergen may be different from another person’s reaction. For instance, one person’s mild reaction to an allergen could trigger a severe attack on another.
Allergies are one of the most common health issues that affect people of all ages. Below are some interesting facts and statistics to put into perspective the prevalence of allergic diseases.
- Globally, adverse drug reactions may affect about 10% of the world’s population and up to 20% of all hospitalized patients.
- Allergies rank 6th among other leading chronic diseases in the U.S.
- In the U.S., allergies affect 30% of adults and 40% of children.
- Around 40 people die in the U.S. every year due to allergic reactions to bee stings.
- Around 10% of the U.S. population is allergic to pets, and cats are often the culprits.
- One study shows that 97.4% of Filipinos exhibit a sensitive response to indoor allergens, with another 86.9% to outdoor allergens.
- Food allergy affects roughly 2.5% of the general population.
- In 2010, there were about 9.4 million reported cases of skin allergies in children.
What is an allergic reaction?
An allergic reaction is the body’s immune system response to fight off foreign elements that are deemed as harmful invaders (even when they are not), like a particular food or substance. These triggers are called allergens, and they can be anything from dust to medication. When the body gets exposed to allergens, it can trigger an allergy attack.
Allergies are more common in children. Some allergies subside and disappear as a child grows older, but many persist throughout their lives. Having an allergy can affect one’s daily routine or activities.
Allergic reactions often happen fast, which may be within a few minutes after exposure to an allergen, and symptoms can vary from mild to severe.
Common symptoms include:
- Stuffy, runny nose, or nasal congestion
- Scratchy throat
- Hay fever, also called allergic rhinitis, causes sneezing, watery eyes, and itching (often triggered by pollen or dust allergens).
- Conjunctivitis or itchy, red, and watery eyes
- Swollen lips, tongue, eyes, face, or contact area
- Raised, itchy, red rashes on the skin (hives)
In some cases, allergies can lead to anaphylaxis, which is a reaction to severe allergies and is a life-threatening condition. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction include:
- Swelling of the face, eyes, or tongue
- Flushing of the face
- Wheezing and difficulty breathing
- Heart palpitations
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Weakness
Types of Allergies
Allergies come in different types. Some are seasonal, and others last year-round. However, there are those that last for a lifetime. Here are the most common types:
Diagnosis
There are two ways to diagnose an allergy:
Treatment
Mild allergic reactions can be treated with over-the-counter medications. Below are the commonly used treatments that alleviate the symptoms of an allergy attack.
- Antihistamine – This medication can treat minor allergic reactions and reduces the common symptoms like watery eyes, stuffy or runny nose, skin reactions, and sneezing. Antihistamines come in different forms, such as oral pills, nasal sprays, eye drops, liquids, and dissolvable tablets.
- Nasal decongestant – To help reduce symptoms like swollen sinuses, sore throat, and stuffy nose, the person can use nasal decongestants like pills, liquids, and sprays. Note that decongestant medications must not be taken continuously for over 72 hours or as prescribed by the doctor.
- Anti-inflammatory medications – For any swelling, cramping, and pain caused by allergic reactions, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can temporarily relieve these.
Naturally, the best way to prevent allergic attacks is to determine the triggers and avoid them, especially with food allergens. If necessary and the symptoms are severe, head to the nearest emergency room for immediate treatment.
Conclusion
Allergens can disrupt one’s daily life and stealthily attack through food or the environment. Everyone should know what to do when someone else experiences an allergic reaction.
If you experience nasal drainage, recurrent sinusitis, coughing, or conditions affecting the ears, nose, and throat, go to an allergologist for a consultation or go straight to an allergologist. It is important to consult with a doctor to identify if you have an allergy or create a plan to manage it. You can contact Makati Medical Center’s allergology and immunology department for urgent health concerns about allergies.