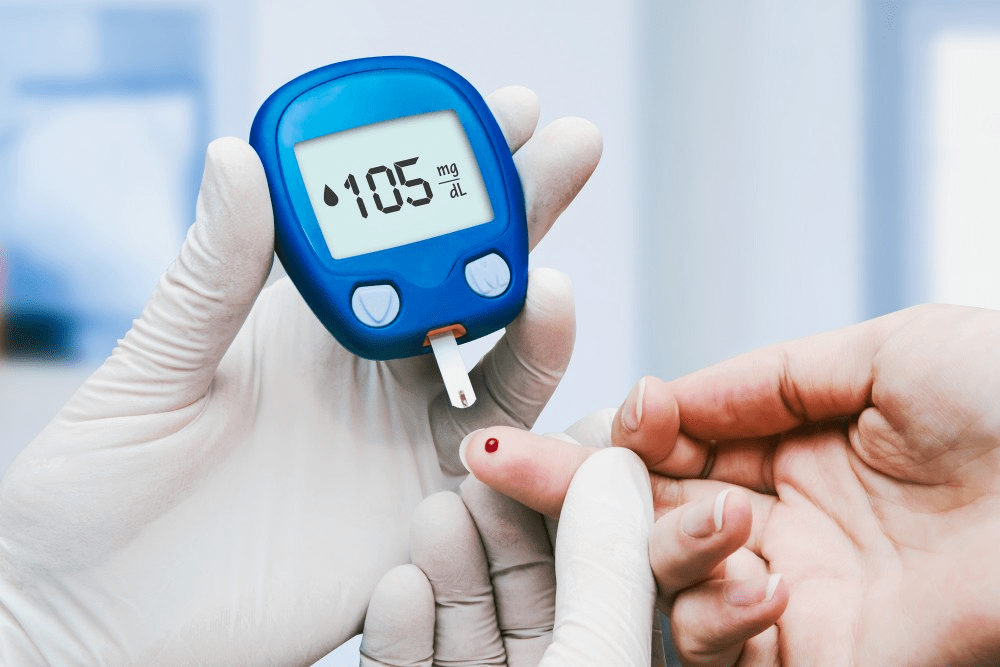
Diabetes is a serious disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is one of the leading causes of death. The numbers below can help better grasp how prevalent it has become.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), roughly 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, with most of them living in low- and middle-income nations.
- About 1.6 million die each year are due to diabetes.
- In the U.S., about 34.2 million people of all ages—around 10.5% of the population—were diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
- In the Philippines, over 5 million people are diagnosed with diabetes.
The disease not only affects the diagnosed physically and mentally, but it also has a significant emotional impact on their families. Those diagnosed can manage diabetes by practicing healthy habits and lifestyle choices to prevent it from becoming a debilitating disorder, so they can spend more years with their loved ones.
Complications from Diabetes
If left undiagnosed and untreated, diabetes can increase the risk of developing several health problems due to complications.
1. Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular problems are common complications for people who fail to manage the condition properly. People with diabetes are twice more likely to develop heart problems such as chest pain, heart attack, stroke, and coronary artery disease than those who do not have it.
Cardiovascular complications are the most common cause of death among people with diabetes. Proper diet and exercise can help prevent these issues or stop them from progressing.
2. Diabetic neuropathy
Nerve damage due to diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy. This is common among people who have had the disease for several years and have progressed to other problems. Keeping blood glucose on the right level can help avoid or delay nerve damage. There are four types of diabetic neuropathy:
- Peripheral neuropathy: This is the most common form and targets the nerves leading to the feet, legs, hands, and arms. Injuries associated with this can lead to severe infections and possible amputations.
- Autonomic neuropathy: This attacks the autonomic nerves, which controls the bladder, genitals, intestinal tract, and other organs. One of its common symptoms is paralysis of the bladder.
- Diabetic amyotrophy: This is a form of neuropathy that causes muscle weakness to the upper part of the legs, buttocks, and hips. It results in nerve pains, especially from the lower back down. Diabetic amyotrophy often affects elderly diabetics.
- Focal Neuropathy: This type affects only one or a group of nerves, causing sudden shooting pain or weakness. It can target the head (causing double vision), paralyze one side of the face (Bell’s palsy), or prompt pain in the torso and legs.
3. Diabetic nephropathy
This pertains to damage in the kidneys, causing it to function less efficiently or fail completely. Increased blood sugar levels make it hard for the kidneys to filter blood, leading to organ damage that leaks protein into the urine, causing a disease called microalbuminuria. Proper diabetes management and blood pressure control can decrease the chance of diabetic nephropathy.
4. Skin disorders
Diabetes complications can hit every part of the body, including the largest organ—the skin. Anyone can be afflicted with skin conditions, but people with diabetes are more susceptible to these due to changes in the small blood vessels and reduced circulation.
Some of the conditions include bacterial or fungal infections, acanthosis nigricans (tan or brown appearance of certain areas), diabetic dermopathy (scaly patches), and more. Fortunately, most skin diseases brought upon by diabetes can be easily treated if discovered early.
5. Eye disease
People with diabetes are also at risk of sight impairment and even blindness. Some of the predominant complications are diabetic retinopathy (disorders in the retina), diabetic macular edema (blurred or complete loss of vision), cataract, and glaucoma. Consistent high levels of blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are the leading causes of eye diseases.
6. Oral disease
If the blood glucose level is not properly managed, people with diabetes are more likely to develop inflammation in the gums (periodontitis). Periodontitis is a primary cause of tooth loss and correlates with an increased risk of heart disease. Oral check-ups for prevention and early diagnosis are crucial to prevention and treatment, especially if symptoms like bleeding and swollen gums occur.
7. Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication that develops when one gets increased levels of ketones that can poison the body. Ketones are chemicals produced when the body starts to burn fat for energy due to the cells not receiving the glucose they need. When ketones build up in the blood, it turns acidic. DKA can advance to diabetic coma or even death when not treated immediately.
8. Pregnancy complications
Diabetic women who are pregnant are at risk of complications if they fail to closely monitor and manage their conditions. They must meet their target glucose levels during pregnancy to avoid health issues and organ damage to the fetus. High blood glucose levels can put excess weight on the fetus and increases their risk of developing diabetes through genetics.
Take Control of Your Diabetes
Keep this disease under control to avoid complications of diabetes and make the condition worse. To prevent further health problems, take medicines religiously, follow a healthy diet, frequently check blood sugar levels, and regularly visit the doctor. If you want to know more about diabetes care, do not hesitate to get in touch with the health professionals at Makati Medical Center.