The COVID-19 crisis has magnified the healthcare system’s crucial role in ensuring public safety. Without a doubt, the hospital is the best place to receive treatment for any health condition, which is why providing high-standard quality healthcare is a must for these institutions.
On the other hand, hospitals can be a high-risk place for patient harm if there is neglect. This makes it of paramount importance to properly train medical professionals and establish strict hospital protocols. From sanitation practices and medical record-keeping, to medication administration and patient diagnosis, getting these things right is all part of patient safety.
What is patient safety?
In plain and simple terms, patient safety is how hospitals and other health care facilities safeguard their patients’ wellness by avoiding errors, injuries or accidents, or wrong judgment calls that may cause harm or endanger lives. The World Health Organization considers patient safety a fundamental discipline that involves every aspect of a comprehensive health care system.
Most hospitals have very stringent standards in maintaining patient safety, but some inadvertently commit lapses. In the United States, medical errors account for 250,000 deaths per year, making it the third leading cause of hospital deaths.
Patient safety in hospitals may cover the following areas.
- Medication errors. When a patient receives the wrong medication, the doctor may have ordered the wrong dosage, put an incorrect entry into the patient’s medical record, or the pharmacy released the wrong prescription.
- Infections due to unsafe medical practices. Hospital-acquired infections may occur due to contaminated tools or surfaces, lack of proper sanitation in care units, or questionable transfusion or surgical procedures.
- Diagnostic errors. Whether a medical team commits an error or a delay in diagnosis, the result generally leads to a patient failing to get the necessary treatment on time.
- Blood clots. These gel-like clumps of blood form naturally as the body tries to stop bleeding due to injury. Doctors should be able to prevent these through various care interventions, including blood thinners or anticoagulants, clot dissolvers, and vein filters.
- Defective devices. Medical errors may stem from faulty medical devices that come with risks of injury or complications for patients.
- Poor flow of information. This can happen when there is insufficient or no proper communication from one hospital unit or service area to another as patients transfer to a different facility or undergo new methods of care.
- Lack of knowledge transfer. New medical staff may lack training opportunities or encounter conflicting information about hospital workflows, preventing them from delivering quality care to patients.
6 Ways Hospitals Ensure Patient Safety While Receiving Treatment
Hospitals can ensure patient safety and prevent untoward harm to patients who seek treatment with these steps.
1. Enforce strict disinfection protocols
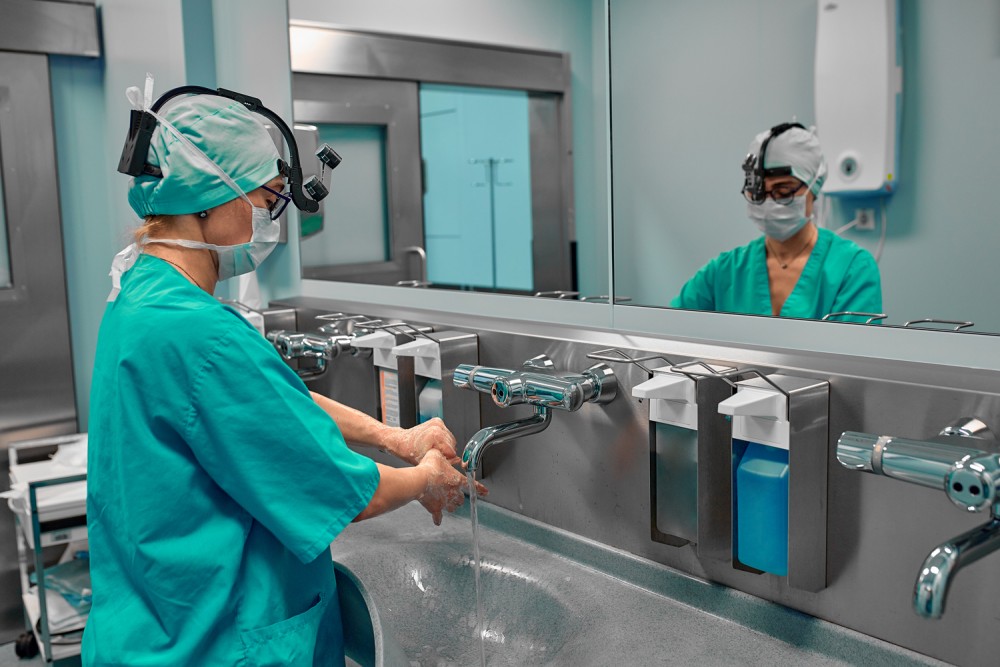
Some ways of preventing the spread of germs in hospitals and other medical facilities include frequent and thorough cleaning of surfaces and high-traffic areas, effective sterilization methods of medical equipment and laboratories, and good hand hygiene, which has been a way of life in MakatiMed.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that healthcare workers on 12-hour shifts clean their hands up to 100 times, depending on the number of patients and the type or level of patient care they provide.
2. Use advanced monitoring equipment
For instance, bed alarms could notify nurses on duty in case a patient falls off the bed or requires medical attention. More accessible nurse call buttons could work better, and electronic systems can be handy in keeping track of patients’ medication needs.
3. Verify all medical procedures
For example, when a patient is scheduled to go under the knife, the physician must conduct a pre-procedure verification process to prevent performing surgery on the wrong person or site. The verification process could also be as simple as asking the staff if they have washed or disinfected their hands before and after entering a patient’s room.
4. Observe care in handling medicines
Doctors should indicate the correct dosage on patients’ prescriptions, while pharmacists and nurses are responsible for dispensing and administering the right medication at the right time, including the brand, strength, and dose.
5. Review staffing policies
6. Work with trusted providers
A Culture of Patient Safety
Medical mistakes and errors may occur, but there are ways to prevent them. Patients need to feel secure that when they go to a hospital, they are getting the best healthcare possible without any risk of harm to their health or, worse, loss of lives.
At Makati Medical Center, patient safety is ingrained in our culture. We guarantee world-class healthcare services to help manage or treat existing medical conditions safely and effectively. There are processes in place that are re-checked and routinely adjusted to the needs and safety of our patients during treatment. Contact us today for any kind of health condition you may have.










