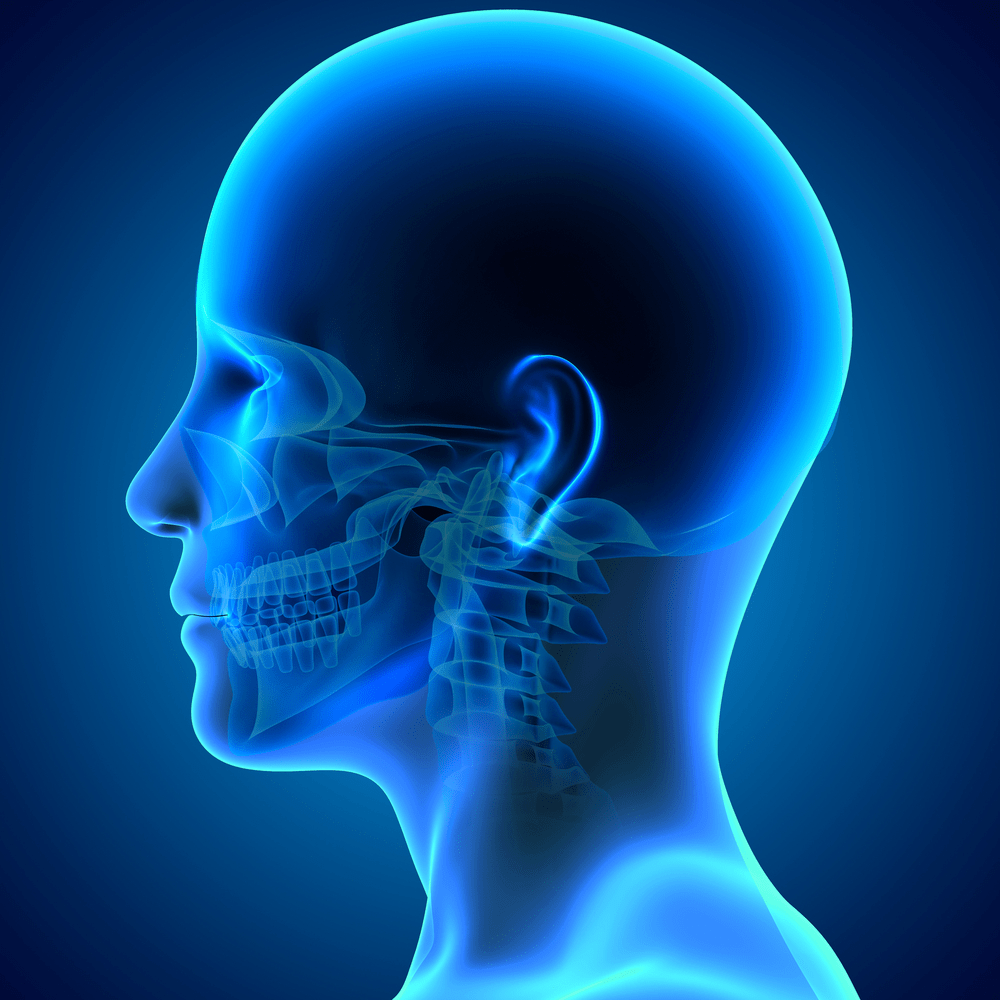
Cancer is a disease that develops due to the uncontrollable growth of abnormal cells. It can develop anywhere in the body, including the head and neck.
Malignant tumors that grow in and around the throat, larynx, nose, sinuses, and mouth are classified as head and neck cancer. Due to its location, the side effects of treatment for head and neck tumors may impair an individual’s ability to eat, swallow, and breathe.
Below is a lowdown on where cancer can develop in the head and neck, its risk factors, and the treatment options available.
Parts of the Head and Neck That can be Affected
Head and neck cancers are categorized by regions of the head and neck where they start to develop.
- Oral cavity – This refers to the lips, anterior two-thirds of the tongue, gums, lining inside the cheeks and lips, bottom of the mouth under the tongue, roof of the mouth, and an area of the gum behind the wisdom teeth.
- Pharynx – This refers to the throat, which is a tube that extends about 5 inches long. It starts behind the nose down to the esophagus. The pharynx has three parts: nasopharynx (upper part of the pharynx, right behind the nose), oropharynx (the middle part of the pharynx, which includes the back of the mouth), and hypopharynx (the bottom part of the pharynx).
- Larynx – This is also known as the voice box, a 2-inch long tube just below the pharynx in the neck. This covers the vocal cords.
- Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavities – This pertains to the small hollow areas in the bones of the head around the nose, while the nasal cavity is the empty space in the nose.
- Salivary glands – These glands that produce saliva rest in the floor of the mouth, close to the jawbone
Five Common Cancers of the Head and Neck
Head and neck cancers have five main types, each of which is named after the part of the body where they form.
1. Oral and oropharyngeal cancers
The oral cavity covers the mouth and the tongue, while the oropharynx includes the tonsils to the tip of the voice box. Oral and oropharyngeal cancers are the eighth most common cancer among men. Signs and symptoms include:
- Soreness in the mouth or on the lip that does not go away (common symptom)
- Red or white patches in the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth
- Lump on the lips, mouth, neck, or throat, and a feeling of thickening inside the cheek
- Lingering sore throat and the feeling that something is caught in the throat
- Hoarseness or change in voice and speech
- Numbness of the mouth or tongue
- Discomfort or bleeding in the mouth
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or moving the jaws or tongue
- Discomfort around the ear or jaw
- Chronic bad breath
- Loosening of teeth or toothache; dentures no longer fit
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite for an extended period, which may occur during the later stages of the disease
2. Nasopharyngeal cancer
This type of cancer occurs in the air passageway at the upper part of the throat behind the nose. About 50% of people diagnosed with this disease are 55 years old or younger. The signs and symptoms include:
- Lump in the neck (common symptom)
- Nasal stuffiness
- Problems with hearing
- Discomfort in the ear caused by a buildup of fluid in the middle ear, often in just one ear
- Pain and ringing in the ear
- Persistent sore throat
- Problems with breathing or speaking; difficulty opening the mouth
- Frequent nosebleeds and headaches
- Discomfort or paralysis of the face
- Blurred or double vision
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
3. Laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer
This type of cancer grows in the voice box (larynx) or the lower part of the throat surrounding the larynx (hypopharynx). In the U.S., statistics show that over 12,300 adults will be diagnosed with laryngeal cancer in 2020. Meanwhile, an estimated 3,000 people are diagnosed with hypopharyngeal cancer each year. Its signs and symptoms include:
- Hoarseness or changes in the voice that persists for weeks (early symptom)
- Lymph nodes or lump in the neck
- Difficulty breathing and noisy breathing
- Persistent sore throat or discomfort in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain in the ear
- Halitosis
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
4. Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer
The nasal cavity rests behind the nose, where air travels on its way to the throat. The paranasal sinuses are the areas around the nasal cavity. Roughly 4 out of 5 people diagnosed with nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer are at least 55 years old. Its signs and symptoms include:
- Persistent nasal congestion and stuffiness or nasal obstruction (sinus congestion)
- Chronic sinus infections that carry on despite antibiotic treatment
- Frequent headaches and pain in the sinus region
- Discomfort or swelling in the face, eyes, or ears
- Tearing of the eyes and bulging of one of the eyes or vision loss
- Declining sense of smell
- Discomfort or numbness in the teeth (or loosening)
- Lump on the face, nose, mouth, and neck
- Frequent runny nose and nosebleeds
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Lump or soreness in the nose that persists
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
5. Salivary gland cancer
From the name itself, this type of cancer develops in the salivary glands. This type of cancer is uncommon but is likely to occur in older people. In the U.S., salivary gland cancer makes up less than 1% of all cancer diagnoses. Its signs and symptoms include:
- Lump on the face, neck, or mouth that is often painless
- Numbness in the face
- Discomfort or swelling in the face, chin, jawbone area, or neck
- Difference in size or shape of the left and right sides of the face or neck
- Progressive facial muscle paralysis
Risk Factors
- Tobacco – Habitual use of tobacco is the biggest risk factor for developing a type of head and neck cancer. Secondhand smoke may also increase this risk. Meanwhile, chewing tobacco has been related to oral cavity cancer.
- Alcohol – Overconsumption of alcohol is the second biggest risk factor for the development of pharyngeal and laryngeal cancers. For those who consume tobacco and alcohol, it can result in a multiplicative increase in risk.
- UV light exposure – Prolonged exposure to UV light may increase the chances of developing lip and oral cancers.
- Exposure to occupational hazards – Some types of head and neck cancers may be associated with occupational exposure. For instance, nasal cancer has been linked to wood dust exposure, while squamous cell cancer of the maxillary sinus has been attributed to nickel exposure.
- Age – Head and neck cancers often affect people over the age of 50.
Treatment
- Surgery – The goal of undergoing a surgical operation is to remove the cancerous tumor and some healthy tissue surrounding it. Depending on the location, stage, and type of cancer, some individuals may require more than one operation. Sometimes, additional treatments may be necessary.
- Chemotherapy – This treatment uses drugs to kill the cancer cells, keep them from growing, and prevent them from dividing and multiplying.
- Radiation therapy – This utilizes high-energy X-rays to eliminate the cancer cells. This therapy can be the primary treatment for head and neck cancer, or it can be done after surgery to kill small areas of cancer that cannot be removed surgically.
- Immunotherapy – Also called biologic therapy, it is designed to enhance the body’s natural defense system to fight cancer.
- Targeted therapy – This treatment attacks cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or tissue environment to stop the growth of cancer.
Head and Neck Cancer: A Serious Disease
Getting diagnosed with cancer and dealing with treatment can be difficult. While this can be irreversible, it can also be a time to view life in a different light—making healthier life choices and changes.
If you are exhibiting symptoms and concerned about your health, you can check out Makati Medical Center’s Otorhinolaryngology Department for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Consult our doctors to find out what you can do to improve your health.